Router BGP Configuration
Before I go too much further, I want to get load balancer services working.
With major cloud vendors that support Kubernetes, creating a service of type LoadBalancer will create a load balancer within that platform that provides external access to that service. This spares us from having to use ClusterIP, etc, to access our services.
This functionality isn't automatically available in a homelab. Why would it be? How could it know what you want? Regardless of the complexities preventing this from Just Working™, this topic is often a source of irritation to the homelabber.
Fortunately, a gentleman and scholar named Dave Anderson spent (I assume) a significant amount of time and devised a system, MetalLB, to bring load balancer functionality to bare metal clusters.
With a reasonable amount of effort, we can configure a router supporting BGP and a Kubernetes cluster running MetalLB into a pretty clean network infrastructure.
Network Architecture Overview
The BGP configuration creates a sophisticated routing topology that enables dynamic load balancer allocation:
Network Segmentation
- Infrastructure CIDR:
10.4.0.0/20(main cluster network) - Service CIDR:
172.16.0.0/20(Kubernetes internal services) - Pod CIDR:
192.168.0.0/16(container networking) - MetalLB Pool:
10.4.11.0/24(load balancer IP range:10.4.11.0 - 10.4.15.254)
BGP Autonomous System Design
- Router ASN:
64500(OPNsense gateway acting as route reflector) - Cluster ASN:
64501(all Kubernetes nodes share this AS number) - Peer relationship: eBGP (External BGP) between different AS numbers
This design follows RFC 7938 recommendations for private AS numbers in the range 64512-65534.
OPNsense Router Configuration
In my case, this starts with configuring my router/firewall (running OPNsense) to support BGP.
Step 1: FRR Plugin Installation
This means installing the os-frr (for "Free-Range Routing") plugin:
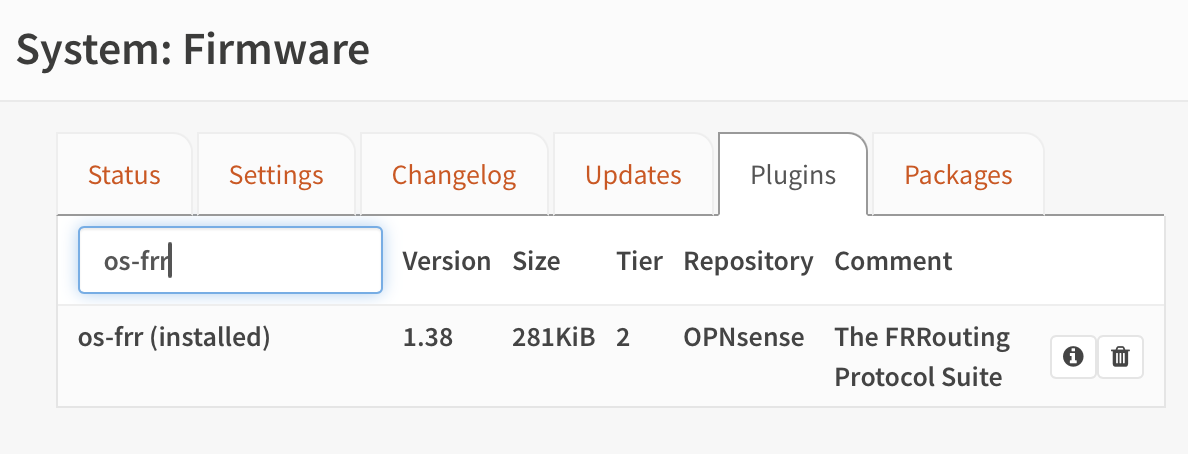
Free-Range Routing (FRR) is a routing software suite that provides:
- BGP-4: Border Gateway Protocol implementation
- OSPF: Open Shortest Path First for dynamic routing
- ISIS/RIP: Additional routing protocol support
- Route maps: Sophisticated traffic engineering capabilities
Step 2: Enable Global Routing
Then we enable routing:
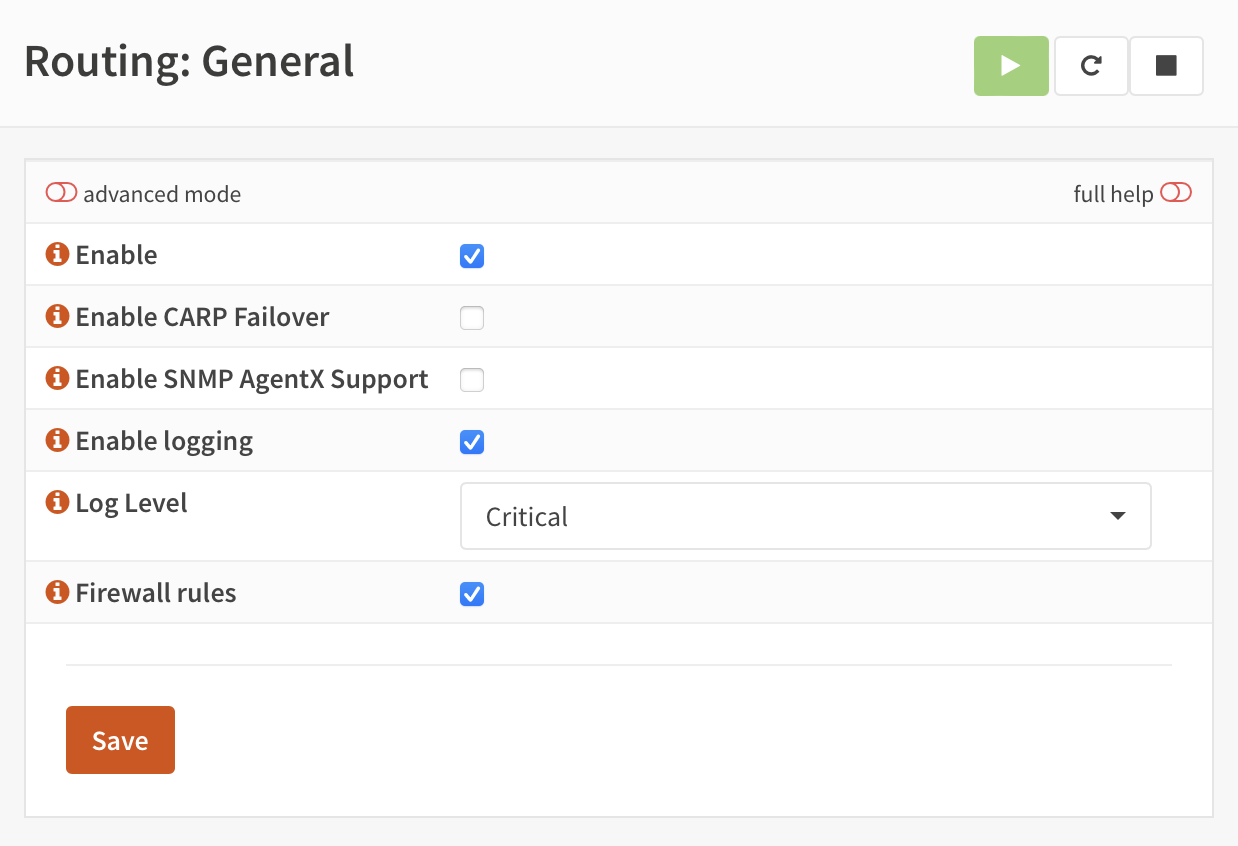
This configuration enables:
- Kernel route injection: FRR can modify the system routing table
- Route redistribution: Between different routing protocols
- Multi-protocol support: IPv4 and IPv6 route advertisement
Step 3: BGP Configuration
Then we enable BGP. We give the router an AS number of 64500.
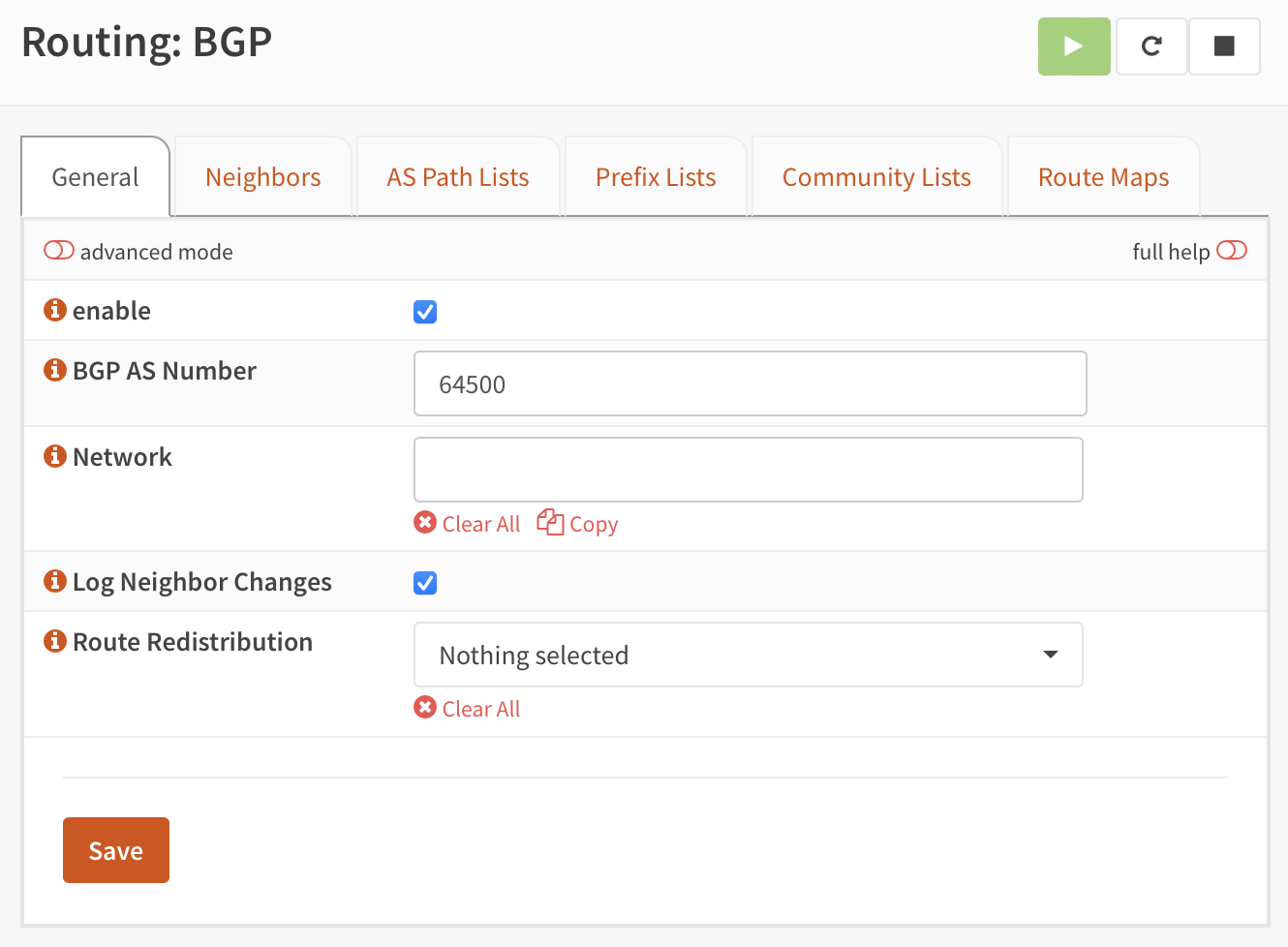
BGP Configuration Parameters:
- Router ID: Typically set to the router's loopback or primary interface IP (
10.4.0.1) - AS Number:
64500(private ASN for the gateway) - Network advertisements: Routes to be advertised to BGP peers
- Redistribution: Connected routes, static routes, and other protocols
Step 4: BGP Neighbor Configuration
Then we add each of the nodes that might run MetalLB "speakers" as neighbors. They all will share a single AS number, 64501.
Kubernetes Node BGP Peers:
# Control Plane Nodes (also run MetalLB speakers)
10.4.0.11 (bettley) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.12 (cargyll) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.13 (dalt) - ASN 64501
# Worker Nodes (potential MetalLB speakers)
10.4.0.14 (erenford) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.15 (fenn) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.16 (gardener) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.17 (harlton) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.18 (inchfield) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.19 (jast) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.20 (karstark) - ASN 64501
10.4.0.21 (lipps) - ASN 64501
10.4.1.10 (velaryon) - ASN 64501
Neighbor Configuration Details:
- Peer Type: External BGP (eBGP) due to different AS numbers
- Authentication: Can use MD5 authentication for security
- Timers: Hold time (180s) and keepalive (60s) for session management
- Route filters: Accept only specific route prefixes from cluster
BGP Route Advertisement Strategy
Router Advertisements
The OPNsense router advertises:
- Default route (
0.0.0.0/0) to provide internet access - Infrastructure networks (
10.4.0.0/20) for internal cluster communication - External services that may be hosted outside the cluster
Cluster Advertisements
MetalLB speakers advertise:
- LoadBalancer service IPs from the
10.4.11.0/24pool - Individual /32 routes for each allocated load balancer IP
- Equal-cost multi-path (ECMP) when multiple speakers announce the same service
Route Selection and Load Balancing
BGP Path Selection
When multiple MetalLB speakers advertise the same service IP:
- Prefer shortest AS path (all speakers have same path length)
- Prefer lowest origin code (IGP over EGP over incomplete)
- Prefer lowest MED (Multi-Exit Discriminator)
- Prefer eBGP over iBGP (not applicable here)
- Prefer lowest IGP cost to BGP next-hop
- Prefer oldest route (route stability)
Router Load Balancing
OPNsense can be configured for:
- Per-packet load balancing: Maximum utilization but potential packet reordering
- Per-flow load balancing: Maintains flow affinity while distributing across paths
- Weighted load balancing: Different weights for different next-hops
Security Considerations
BGP Session Security
- MD5 Authentication: Prevents unauthorized BGP session establishment
- TTL Security: Ensures BGP packets come from directly connected neighbors
- Prefix filters: Prevent route hijacking by filtering unexpected announcements
Route Filtering
# Example prefix filter configuration
prefix-list METALLB-ROUTES permit 10.4.11.0/24 le 32
neighbor 10.4.0.11 prefix-list METALLB-ROUTES in
This ensures the router only accepts MetalLB routes within the designated pool.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
BGP Session Monitoring
Key commands for BGP troubleshooting:
# View BGP summary
vtysh -c "show ip bgp summary"
# Check specific neighbor status
vtysh -c "show ip bgp neighbor 10.4.0.11"
# View advertised routes
vtysh -c "show ip bgp advertised-routes"
# Check routing table
ip route show table main
Common BGP Issues
- Session flapping: Often due to network connectivity or timer mismatches
- Route installation failures: Check routing table limits and memory
- Asymmetric routing: Verify return path routing and firewalls
Integration with MetalLB
The BGP configuration on the router side enables MetalLB to:
- Establish BGP sessions with the cluster gateway
- Advertise LoadBalancer service IPs dynamically as services are created
- Withdraw routes automatically when services are deleted
- Provide redundancy through multiple speaker nodes
This creates a fully dynamic load balancing solution where:
- Services get real IP addresses from the external network
- Traffic routes optimally through the cluster
- Failover happens automatically via BGP reconvergence
- No manual network configuration required for new services
In the next section, we'll configure MetalLB to establish these BGP sessions and begin advertising load balancer routes.